COMPARATIVE GENOMICS
Image source:-genome.gov
Comparative genomics is a field of organic studies in which the genomic functions of various organisms are in comparison. The genomic functions may additionally consist of the DNA collection, genes, gene order, regulatory sequences, and different genomic structural landmarks.
In this department of genomics, complete or big elements of genomes as a consequence of genome initiatives are in comparison to take a look at basic biological similarities and differences as well as evolutionary relationships between organisms.
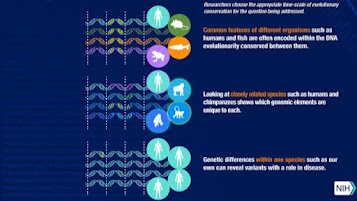
The essential precept of comparative genomics is that commonplace capabilities of organisms will often be encoded within the DNA that is evolutionarily conserved between them.
Therefore, comparative genomic strategies begin with making a few shape of alignment of genome sequences and looking for orthologous sequences (sequences that share a not unusual ancestry) within the aligned genomes and checking to what extent the ones sequences are conserved.
Based on those, genome and molecular evolution are inferred and this could in flip be put within the context of, as an example, phenotypic evolution or population genetics.
BENEFITS OF COMPETITIVE GENOMICS
Identifying
DNA sequences that have been "conserved" - this is, preserved in many exceptional organisms over hundreds of thousands of years - is an crucial step closer to know-how the genome itself.
It pinpoints genes which might be crucial to lifestyles and highlights genomic alerts that control gene characteristic across many species. It facilitates us to similarly recognize what genes relate to diverse organic structures, which in turn may additionally translate into modern tactics for treating human sickness and improving human fitness.
Comparative genomics additionally presents a effective device for studying evolution. By taking advantage of - and studying- the evolutionary relationships between species and the corresponding differences of their DNA, scientists can higher recognize how the advent, conduct and biology of dwelling matters have modified over the years.
As DNA sequencing generation will become greater powerful and much less high-priced, comparative genomics is finding wider packages in agriculture, biotechnology and zoology as a device to tease aside the frequently diffused variations amongst animal species.
Such efforts have caused new insights into a few branches on the evolutionary tree, as well as enhancing the fitness of domesticated animals and pointing to new techniques for keeping uncommon and endangered species.
METHODS OF COMPARATIVE GENOMICS
Computational techniques to genome assessment have recently end up a commonplace studies topic in computer technology. A public collection of case studies and demonstrations is developing, starting from whole genome comparisons to gene expression analysis.
This has extended the advent of different thoughts, including concepts from structures and manage, information concept, strings analysis and information mining.
It is predicted that computational strategies becomes and remain a standard topic for research and coaching, at the same time as a couple of courses will start schooling college students to be fluent in both topics.
TOOLS FOR COMPARATIVE GENOMICS
Computational tools for reading sequences and entire genomes are growing fast due to the supply of large quantity of genomic statistics. At the identical time, comparative analysis tools are progressed and advanced. In the demanding situations approximately these analyses, it is very critical to visualise the comparative outcomes.
Visualization of sequence conservation is a difficult assignment of comparative sequence evaluation. As we recognize, it's miles distinctly inefficient to examine the alignment of long genomic areas manually.
Internet-primarily based genome browsers provide many beneficial equipment for investigating genomic sequences because of integrating all collection-based totally organic information on genomic regions. When we extract massive amount of relevant biological information, they can be very easy to use and much less time-consuming.
1:-UCSC Browser: This site incorporates the reference collection and operating draft assemblies for a large series of genomes.
2:-Ensembl: The Ensembl project produces genome databases for vertebrates and other eukaryotic species, and makes this information freely available on-line.
3:-MapView: The Map Viewer offers a wide form of genome mapping and sequencing facts.
4:-VISTA : Vista is a complete suite of programs and databases for comparative evaluation of genomic sequences. It turned into constructed to visualize the results of comparative evaluation based totally on DNA alignments. The presentation of comparative facts generated with the aid of VISTA can without difficulty match both small and massive scale of records.
5:-BlueJay Genome Browser: a stand-by myself visualization device for the multi-scale viewing of annotated genomes and different genomic elements.
An gain of the use of online tools is that these web sites are being developed and updated constantly. There are many new settings and content material may be used on-line to improve performance.
SEQUENCED GENOMES
Researchers have sequenced the complete genomes of many of animals and plants -more than 250 animal species and 50 species of birds alone-and the listing maintains to grow nearly each day.
In addition to the sequencing of the human genome, which changed into finished in 2003, scientists involved within the Human Genome Project sequenced the genomes of a number of version organisms which can be usually used as surrogates in studying human biology.
These encompass the rat, puffer fish, fruit fly, sea squirt, roundworm, and the bacterium Escherichia coli. For some organisms NHGRI has sequenced many sorts, imparting vital records for information genetic version.
DNA sequencing facilities supported through NHGRI also have sequenced genomes of the fowl, canine, honey bee, gorilla, chimpanzee, sea urchin, fungi and many other organisms.
APPLICATION OF COMPARATIVE GENOMICS
Agriculture
Agriculture is a subject that reaps the benefits of comparative genomics. Identifying the loci of nice genes is a key step in breeding crops which are optimized for greater yield, value-efficiency, first-rate, and disorder resistance. For instance, one genome extensive affiliation study conducted on 517 rice landraces found out 80 loci associated with several classes of agronomic performance, inclusive of grain weight, amylose content material, and drought tolerance. Many of the loci were formerly uncharacterized.
Not most effective is this technique powerful, it's also quick. Previous techniques of identifying loci associated with agronomic overall performance required numerous generations of carefully monitored breeding of parent lines, a time eating attempt this is unnecessary for comparative genomic studies.
Medicine
The clinical field additionally blessings from the have a look at of comparative genomics. Vaccinology especially has experienced useful advances in era because of genomic strategies to problems.
In an method known as reverse vaccinology, researchers can discover candidate antigens for vaccine development through reading the genome of a pathogen or a own family of pathogens.
Applying a comparative genomics method by way of reading the genomes of numerous related pathogens can cause the development of vaccines that are multiprotective. A team of researchers hired such an approach to create a normal vaccine for Group B Streptococcus, a set of bacteria accountable for excessive neonatal contamination.
Comparative genomics can also be used to generate specificity for vaccines against pathogens which are closely related to commensal microorganisms. For example, researchers used comparative genomic analysis of commensal and pathogenic lines of E. Coli to pick out pathogen precise genes as a basis for locating antigens that bring about immune response towards pathogenic strains however not commensal ones.
In May of 2019, the usage of the Global Genome Set, a group within the UK and Australia sequenced thousands of globally-amassed isolates of Group A Streptococcus, presenting capability objectives for developing a vaccine towards the pathogen, also referred to as S. Pyogenes.
Research
Comparative genomics also opens up new avenues in other areas of studies. As DNA sequencing era has become greater reachable, the quantity of sequenced genomes has grown. With the growing reservoir of available genomic statistics, the efficiency of comparative genomic inference has grown as well.
A wonderful case of this elevated potency is discovered in current primate studies. Comparative genomic techniques have allowed researchers to collect facts approximately genetic variation, differential gene expression, and evolutionary dynamics in primates that have been indiscernible the use of preceding statistics and methods.
Great Ape Genome Project
The Great Ape Genome Project used comparative genomic strategies to investigate genetic version with reference to the six splendid ape species, locating wholesome ranges of variant in their gene pool no matter shrinking populace length.
Another examine showed that styles of DNA methylation, that are a recognised regulation mechanism for gene expression, vary in the prefrontal cortex of humans versus chimps, and implicated this distinction inside the evolutionary divergence of the 2 species.
ABOUT NHGRI PROGRAMS
NHGRI pioneered the improvement of DNA sequencing strategies and technology - which includes informatics - and has funded research to study the genomes of a huge range of species. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) Intramural Sequencing Center has been instrumental in the sequencing of many organisms.
NHGRI programs which include ENCODE (Encyclopedia of DNA Elements) and modENCODE (version organism Encyclopedia of DNA Elements) have compared and contrasted the internal workings of animal and human genomes to try to better recognize how genomes feature.
In modENCODE, researchers discovered shared patterns of gene interest and law amongst fly, worm and human genomes. The mouse ENCODE Consortium demonstrated that, in standard, the systems which are used to govern gene activity have many similarities in mice and humans.










Excellent
ReplyDeleteSupar
ReplyDeleteThank you for your response 😊😊
ReplyDeleteNice
ReplyDelete